De belofte van Schrage
Wij leven en houden van uw bulkgoedtransport. Daarom gaat het ons echt aan het hart om u te ondersteunen.
Ons team controleert en test uw eisen grondig. Wij bieden een oplossing alleen aan wanneer deze u voordeel biedt.
Want u vindt bij ons geen confectieproducten, maar deugdelijke oplossingen.
Type 115
| Q (m³/h) | 1,25 | 2,00 | 2,65 | 4,00 | 5,50 | 7,00 | 8,75 | 10,60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (kW) | 0,75 | 1,10 | 1,50 | 2,20 | 3,00 | 4,00 | 4,00 | 5,50 |
| V (m/s) | 0,06 | 0,09 | 0,13 | 0,19 | 0,26 | 0,33 | 0,42 | 0,51 |
| n (1/min) | 3,20 | 5,40 | 7,30 | 11,00 | 15,00 | 19,00 | 24,00 | 29,00 |
Type 135
| Q (m³/h) | 2,30 | 3,65 | 4,90 | 7,40 | 10,10 | 12,75 | 16,10 | 19,45 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (kW) | 0,75 | 1,10 | 1,50 | 2,20 | 3,00 | 4,00 | 4,00 | 5,50 |
| V (m/s) | 0,06 | 0,09 | 0,13 | 0,19 | 0,26 | 0,33 | 0,42 | 0,51 |
| n (1/min) | 3,20 | 5,40 | 7,30 | 11,00 | 15,00 | 19,00 | 24,00 | 29,00 |
Type 160
| Q (m³/h) | 1,10 | 2,30 | 4,00 | 5,20 | 8,50 | 11,20 | 14,70 | 19,00 | 21,00 | 25,30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (kW) | 0,55 | 0,75 | 1,50 | 2,20 | 2,20 | 4,00 | 4,00 | 5,50 | 5,50 | 7,50 |
| V (m/s) | 0,02 | 0,04 | 0,07 | 0,09 | 0,15 | 0,20 | 0,26 | 0,33 | 0,37 | 0,45 |
| n (1/min) | 1,00 | 2,00 | 3,30 | 4,20 | 7,00 | 9,20 | 12,00 | 15,00 | 17,00 | 21,00 |
Type 200
| Q (m³/h) | 1,80 | 3,70 | 6,40 | 8,20 | 13,50 | 17,90 | 23,40 | 30,10 | 33,40 | 40,20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (kW) | 0,55 | 0,75 | 1,50 | 2,20 | 2,20 | 4,00 | 4,00 | 5,50 | 5,50 | 7,50 |
| V (m/s) | 0,02 | 0,04 | 0,07 | 0,09 | 0,15 | 0,20 | 0,26 | 0,33 | 0,37 | 0,45 |
| n (1/min) | 1,00 | 2,00 | 3,30 | 4,20 | 7,00 | 9,20 | 12,00 | 15,00 | 17,00 | 21,00 |
Type 270
| Q (m³/h) | 14,60 | 33,30 | 45,10 | 61,60 | 80,80 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (kW) | 3,00 | 5,50 | 7,50 | 11,00 | 15,00 |
| V (m/s) | 0,10 | 0,22 | 0,30 | 0,41 | 0,54 |
| n (1/min) | 3,60 | 8,30 | 11,00 | 16,00 | 21,00 |
Use of tube chain conveyors
Schrage tube chain conveyors are conveyor systems for a wide variety of industries. It is possible to transport abrasive, toxic, explosive, or adhesive bulk material or even materials with high temperatures.
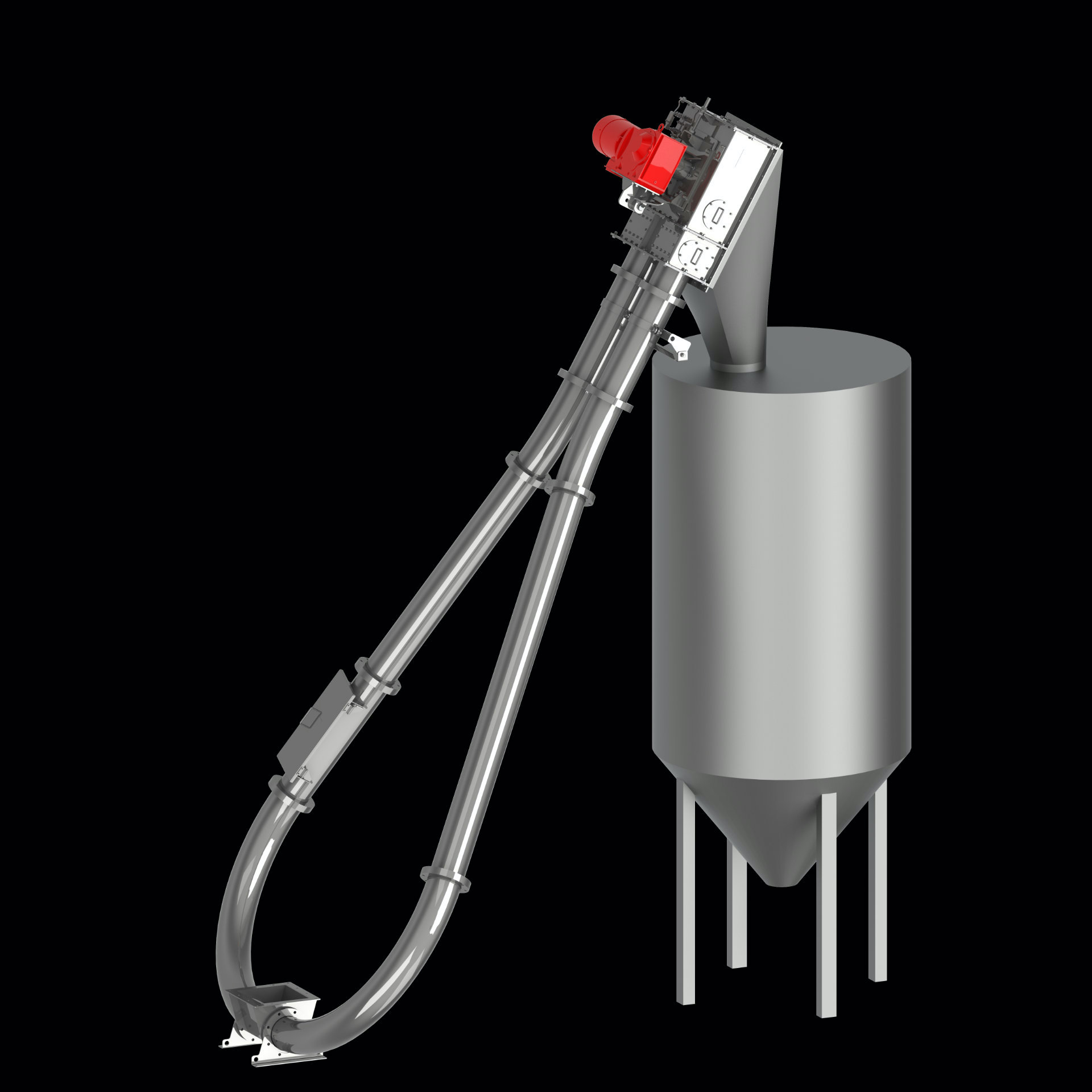
The tube conveyor is available in different designs: horizontal, vertical, diagonal, or a combination thereof and in five different sizes: 115, 135, 160, 200, and 270. It is in this way that the layout, speed, and materials can be optimally adjusted to suit your bulk material.
The conveyor system transports bulk material with grain sizes of up to 100 mm, a bulk density of up to 5 t/m³ or more, and flow rates of up to 80 m³/h. The maximum size per leg is 50 m horizontally or 30 m vertically.
The advantages of the modular chain conveyors are their flexibility and nearly unlimited application possibilities, such as easy vertical conveyance, multiple inlets and outlets, or the conveyance of bulk materials in two directions simultaneously.
The low chain speed is perfect for ensuring the gentle handling of the products. The conveyor system is absolutely dust-tight with a high selfcleaning capacity and virtually no dead space and, if necessary, can be designed to meet all the ATEX requirements. Schrage chain conveyers feature low maintenance, easy handling, and high operational reliability. They require very little space and will quickly pay for themselves due to their low energy requirements and low operational costs.
The conveyor system
Tube chain conveyors are mechanical conveyor systems used for conveying bulk materials, and are classified as continuous conveyors with a continuous traction element loop.
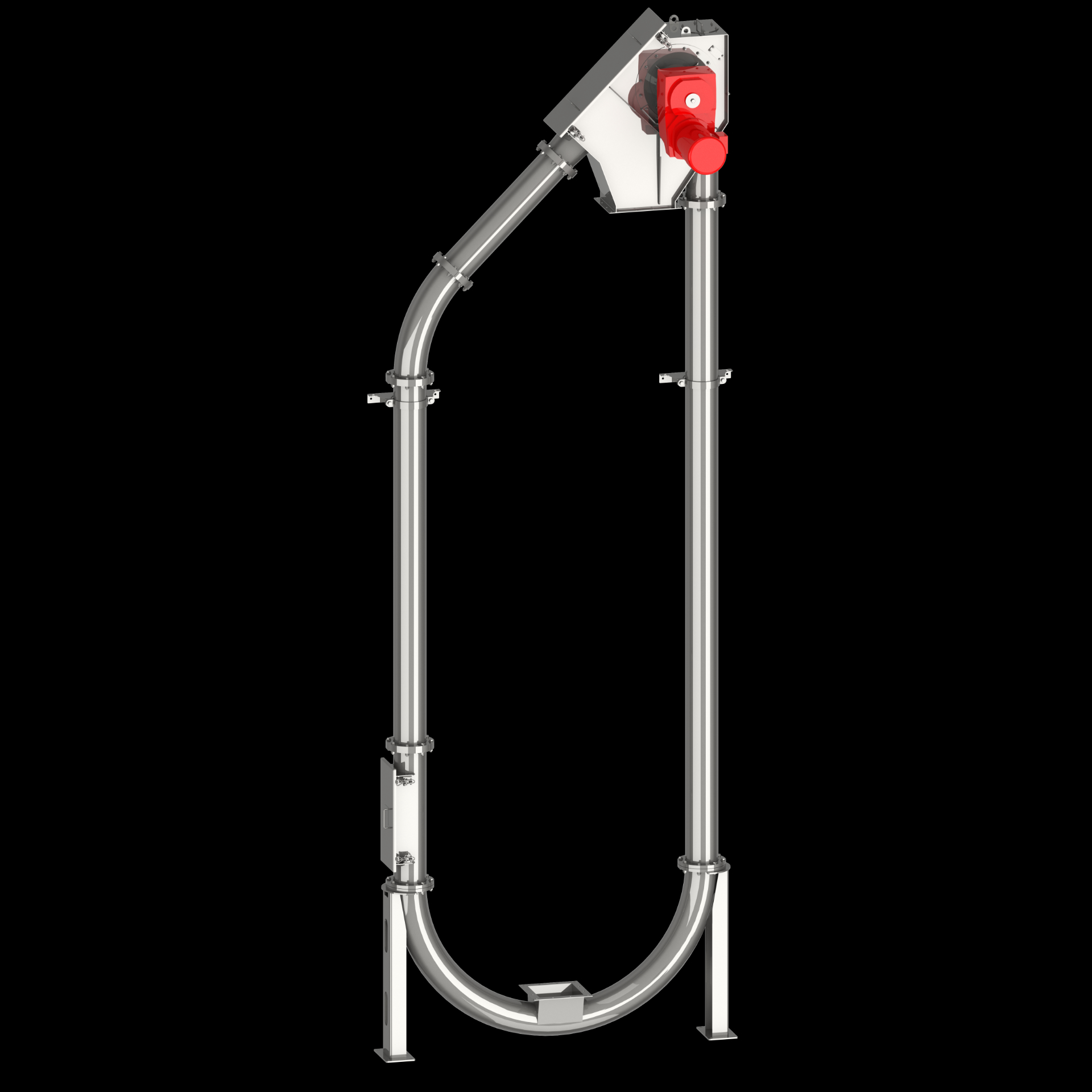
In contrast to conventional materials handling equipment, the chain conveyors make it possible to convey materials horizontally, vertically, diagonally, or with a combination of any of These three possibilities. Thus they can smoothly be integrated into nearly any space. Indeed, their three-dimensional design makes it possible to adapt them to almost any set of operational conditions.
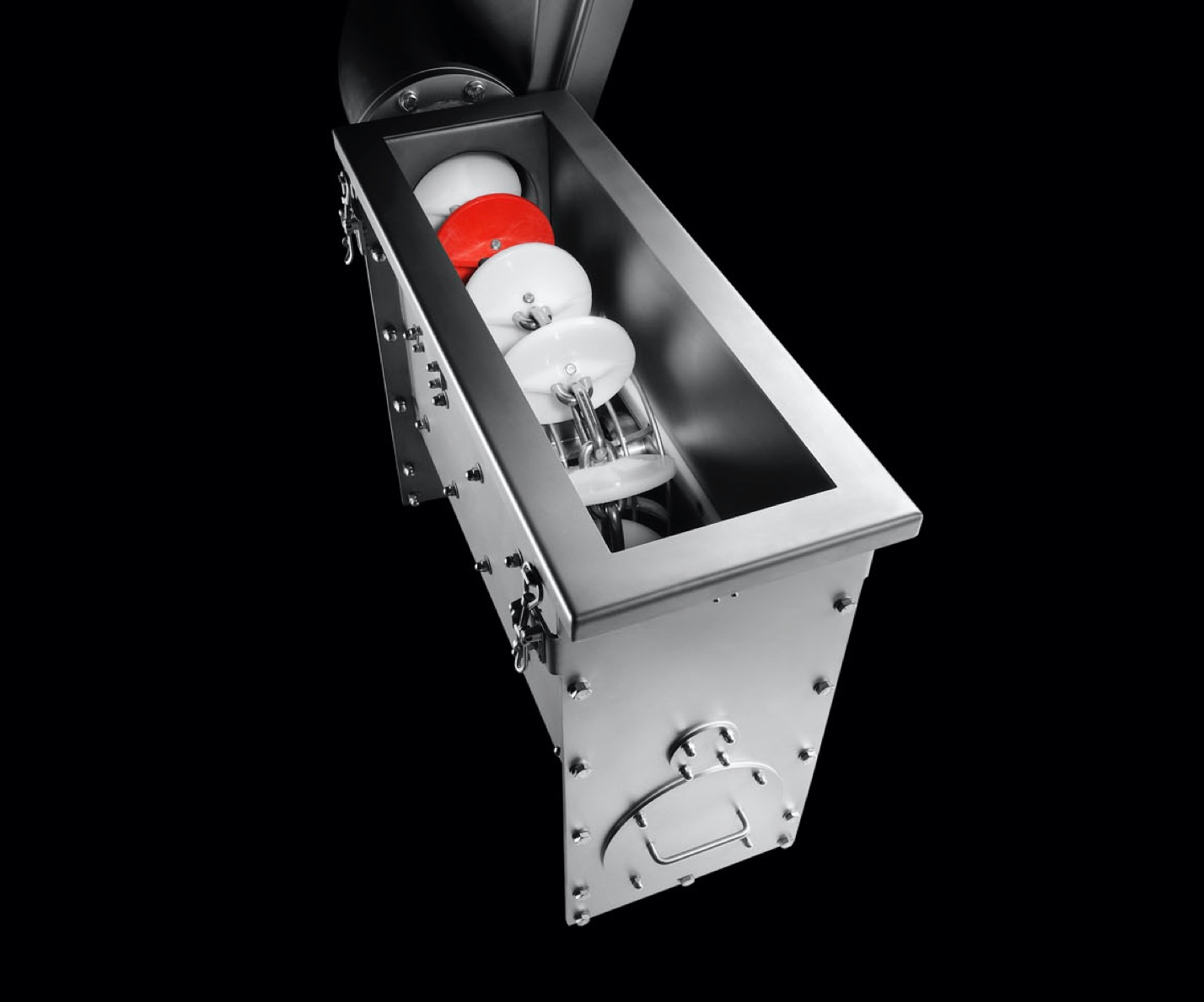
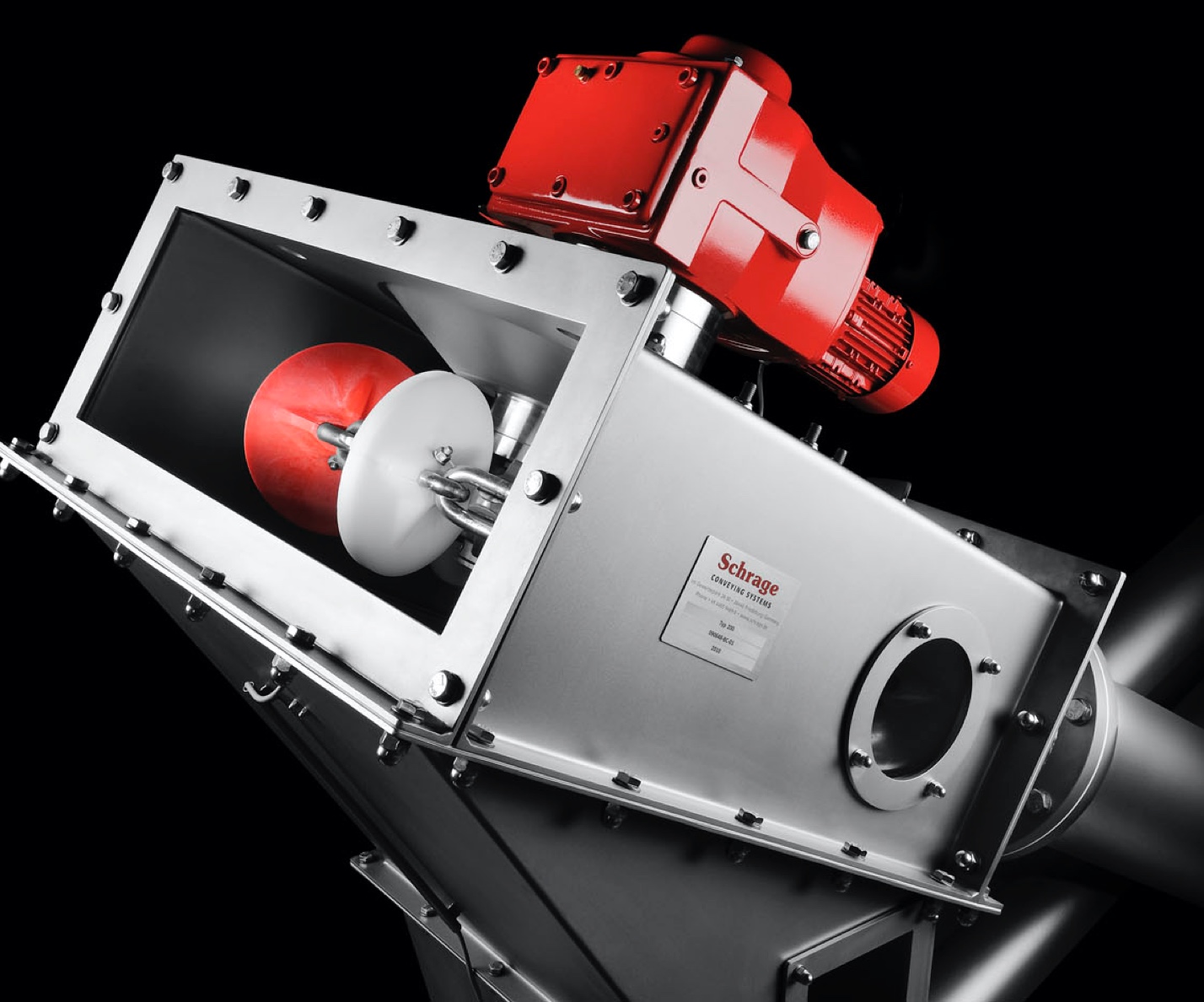
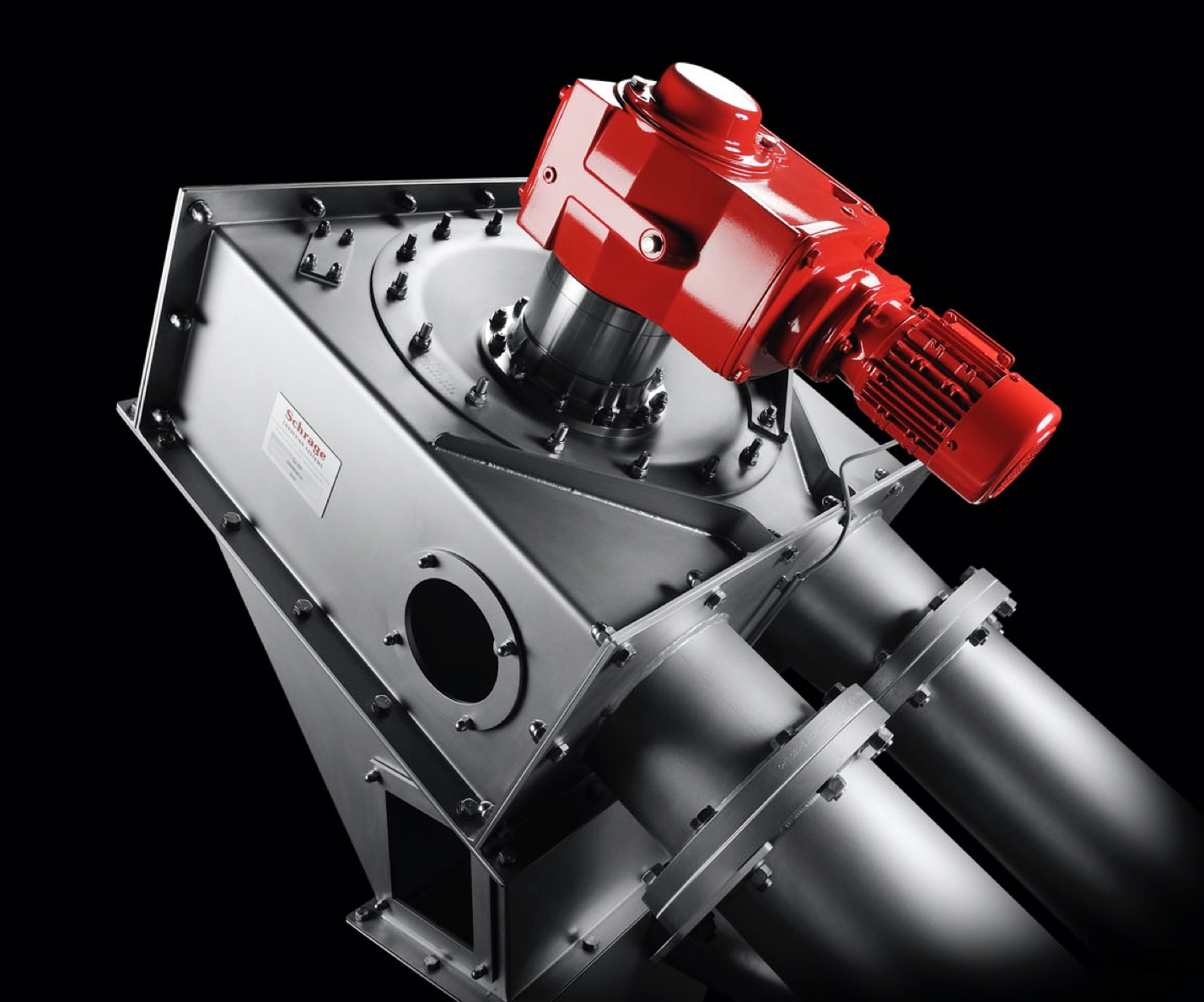
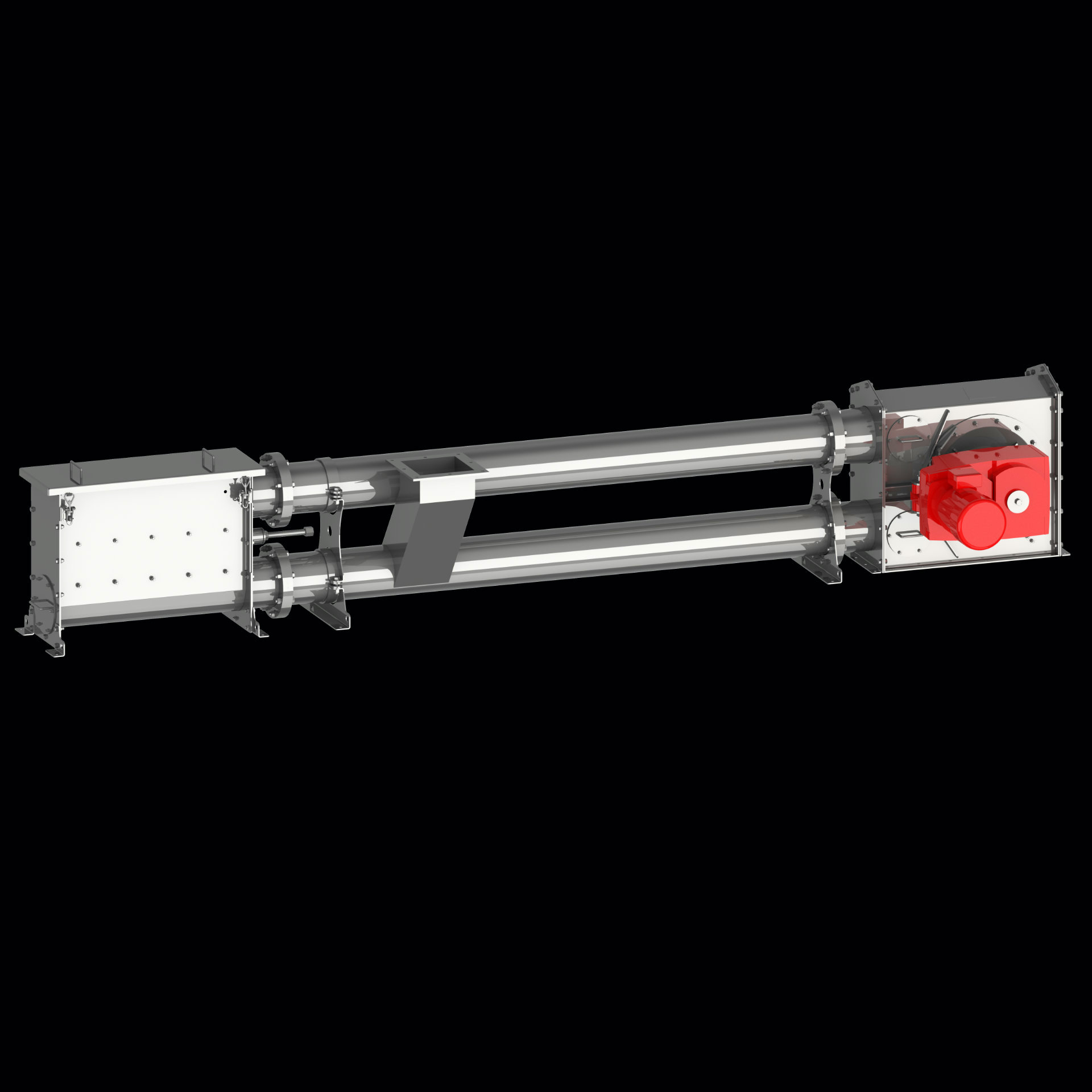
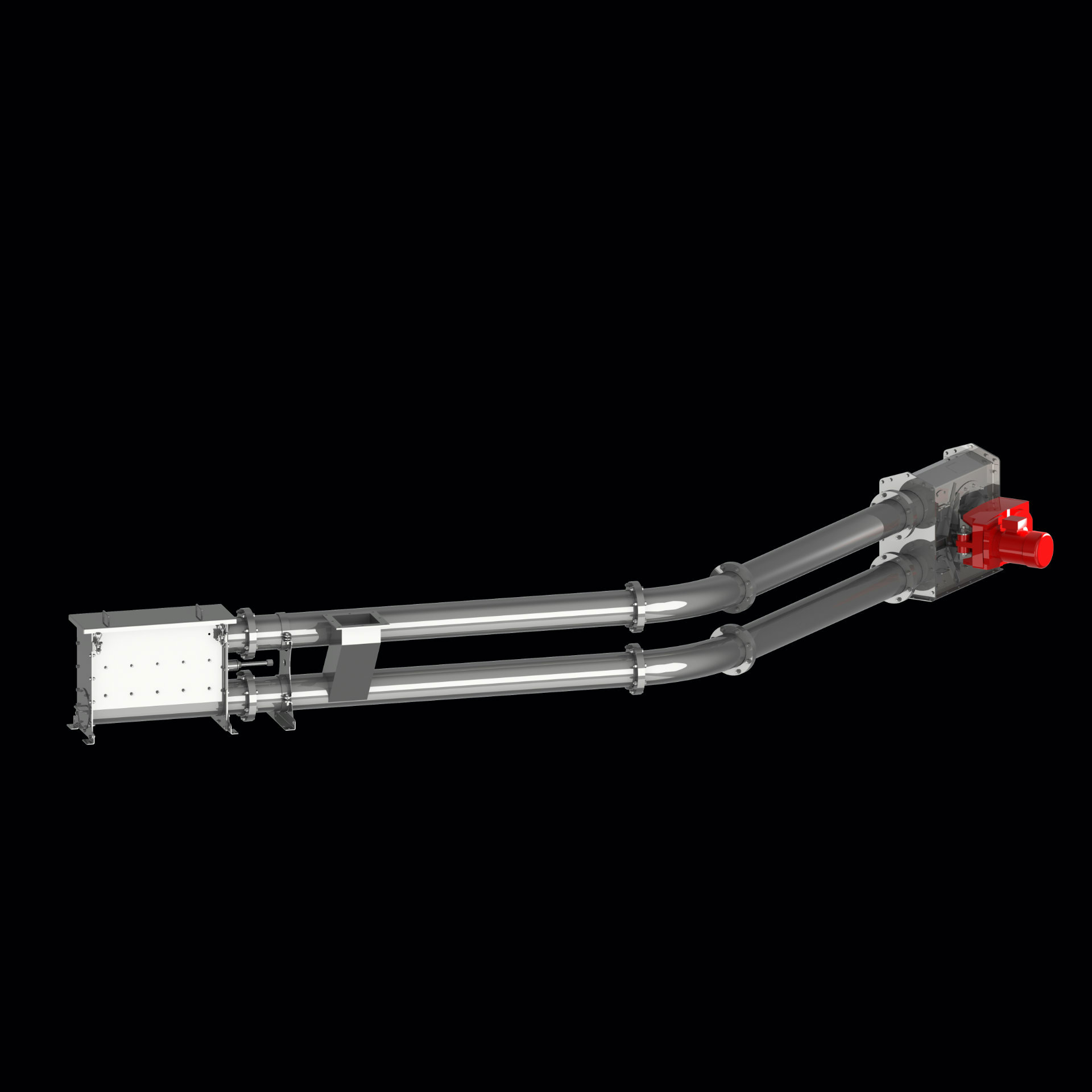
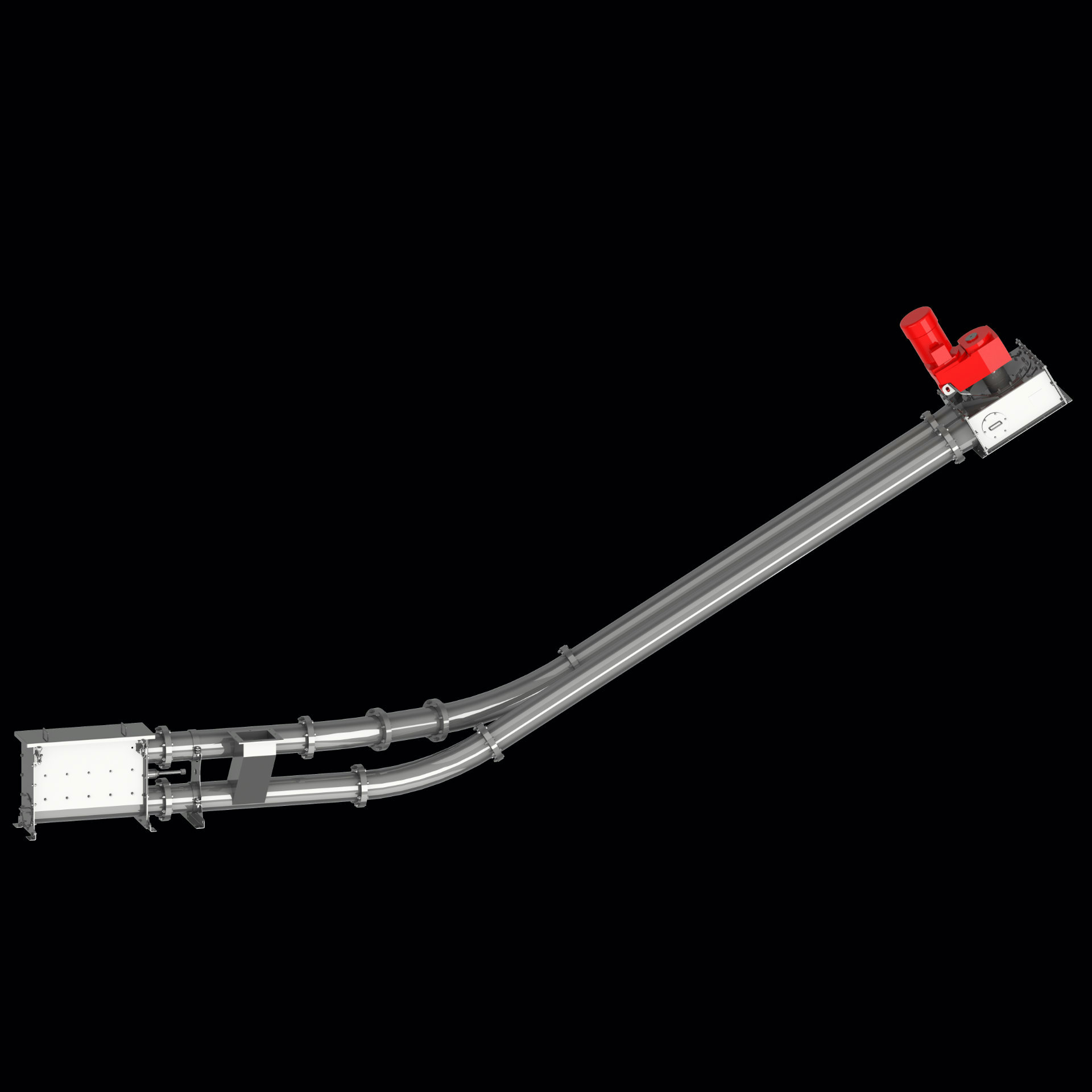
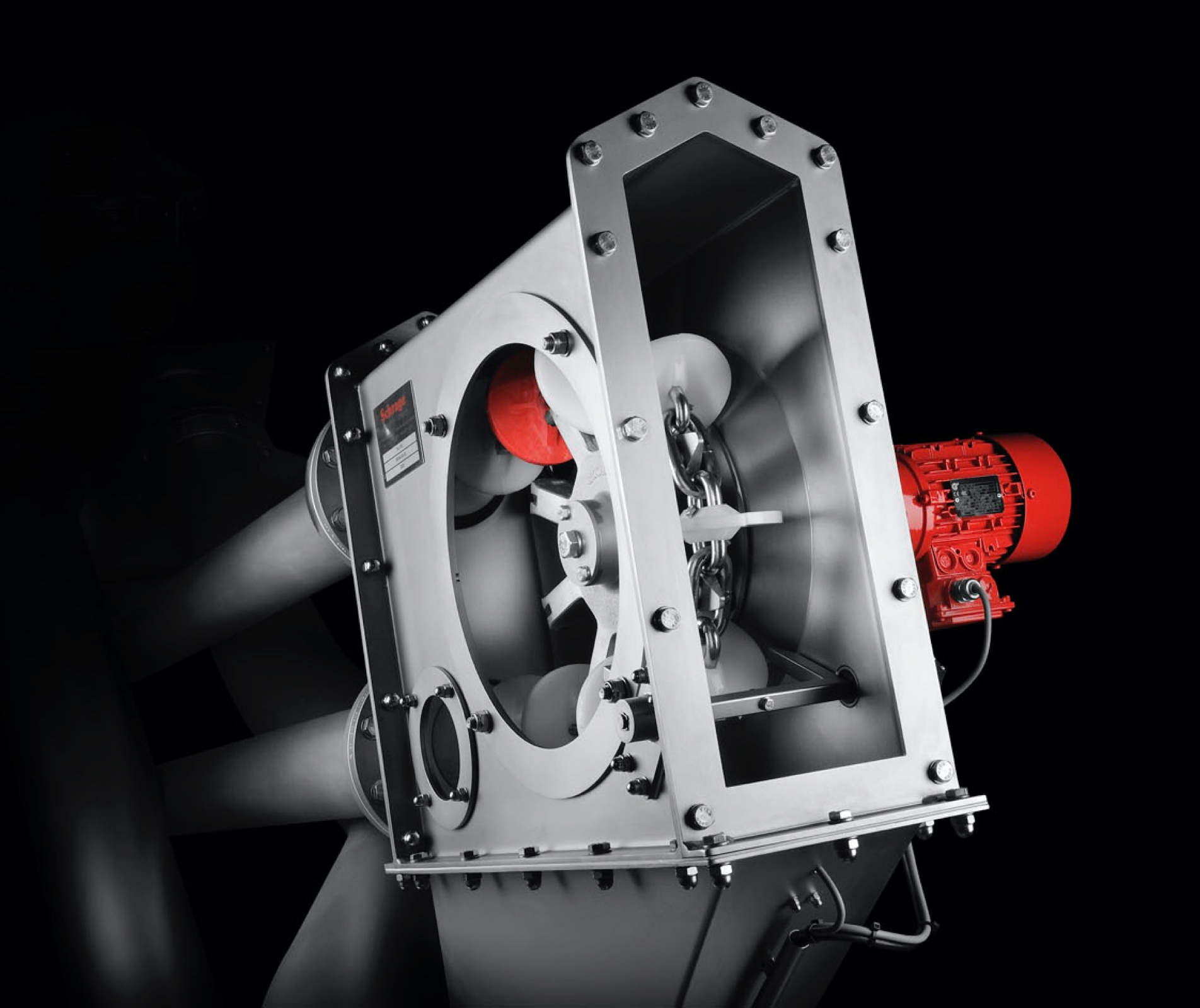
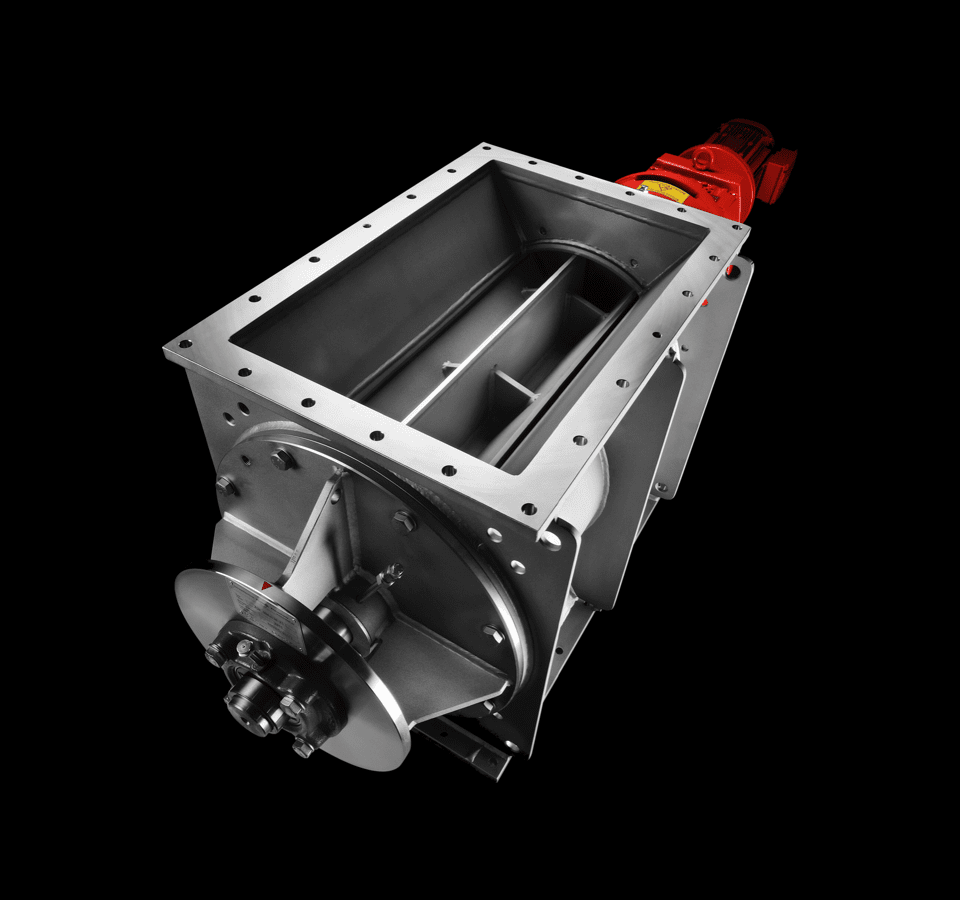
A tube chain conveyor’s basic components include a tension station, a drive station, a tube on the conveying and return path sides, and an endless conveyor chain with transport discs attached at regular intervals.
The conveyor chain is guided through the tube, conveying material in an extremely gentle manner during the process. Meanwhile, the various conveyor discs create what is called “pocket structure,” which is responsible for relieving positive or negative pressure in the system, as the case may be.
Normally, the inlet used to feed bulk material is placed near the tensioning station, in the conveying path, while the discharge outlet is located underneath the drive station.
The enclosed design makes tube chain conveyors dustproof, gas- and pressure-tight.
In addition, it allows for the clean conveyance of bulk materials and for any number of outlets and inlets to be integrated into a single conveyor.
Maten
In order to ensure that our tube chain conveyors would be capable of handling a large variety of delivery rates, we developed five different model sizes. In fact, their names are derived from each unit’s tube diameter, which is why we have the 115, 135, 160, 200, and 270 tube chain conveyor models. The different model sizes make it possible to convey bulk solids with a grain size of up to 100 mm, bulk densities of over 5 t/m³, and throughputs of up to 80 m³/h.
Additional factors that must be taken into account when selecting a tube chain conveyor include the relevant material’s characteristics (e.g., temperature, bulk weight, moisture, grain size, and special properties such as abrasiveness, adhesiveness, etc.) and the conveyor route’s direction and length. Under normal conditions, a tube conveyor’s length is limited to 50 m (horizontally) or 30 m (vertically).
Tube chain conveyors are available in various configurations, which can also be combined with each other:
- In a flat position (tubes next to each other)
- With an upright design (tubes on top of each other)
- And/or in vertical arrangements
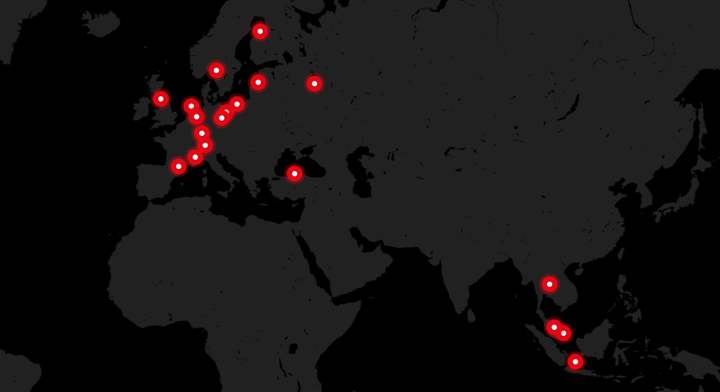
The fact that tube chain conveyors are designed in the form of space-saving, cost-effective modular systems has made them a popular choice in nearly all industries and industry applications, including: aluminium mills, construction material plants, breweries, chemical plants, the fertilizer industry, paint plants, the meat meal industry, plaster factories, cogeneration plants, lime plants, the ceramics industry, sewage treatment plants, the concentrated feed industry, power plants, the plastics industry, the food industry, incineration plants, paper mills, carbon black plants, steel mills, rendering, the laundry detergent industry, the cement industry.
Advantages of tube chain conveyors
in comparison to conventional material handling equipment:
- Flexible line layout (three-dimensional)
- Dust-proof, gas-tight, and pressure-tight conveyance
- Conveyance of highly abrasive, toxic, explosive, adhesive, and chemically aggressive materials
- Can be made food-safe
- Low power requirements (e.g., a rate of 60 m³/h with a horizontal length of 50 m or a vertical length of 30 m would require 9.2 kW only)
- Dust-ignition-proof
- Resistance to explosive blasts
- All designs can be made to conform to ATEX
- Resistance to pressure surges
- Low maintenance requirements, a long service life, and low wear due to low chain speeds
- They require little space
- Negligible destruction of grains and friable materials, gentle conveyance
- Forced discharge possible with adhesive materials as well
- High level of self-cleaning (no dead zones)
- Homogenous silo filling (no segregation)
- Can be restarted while full
- High degree of efficiency in discarding residues, making it possible to change the materials being conveyed
For more details: Comparison between various technologies
Verticaal transport
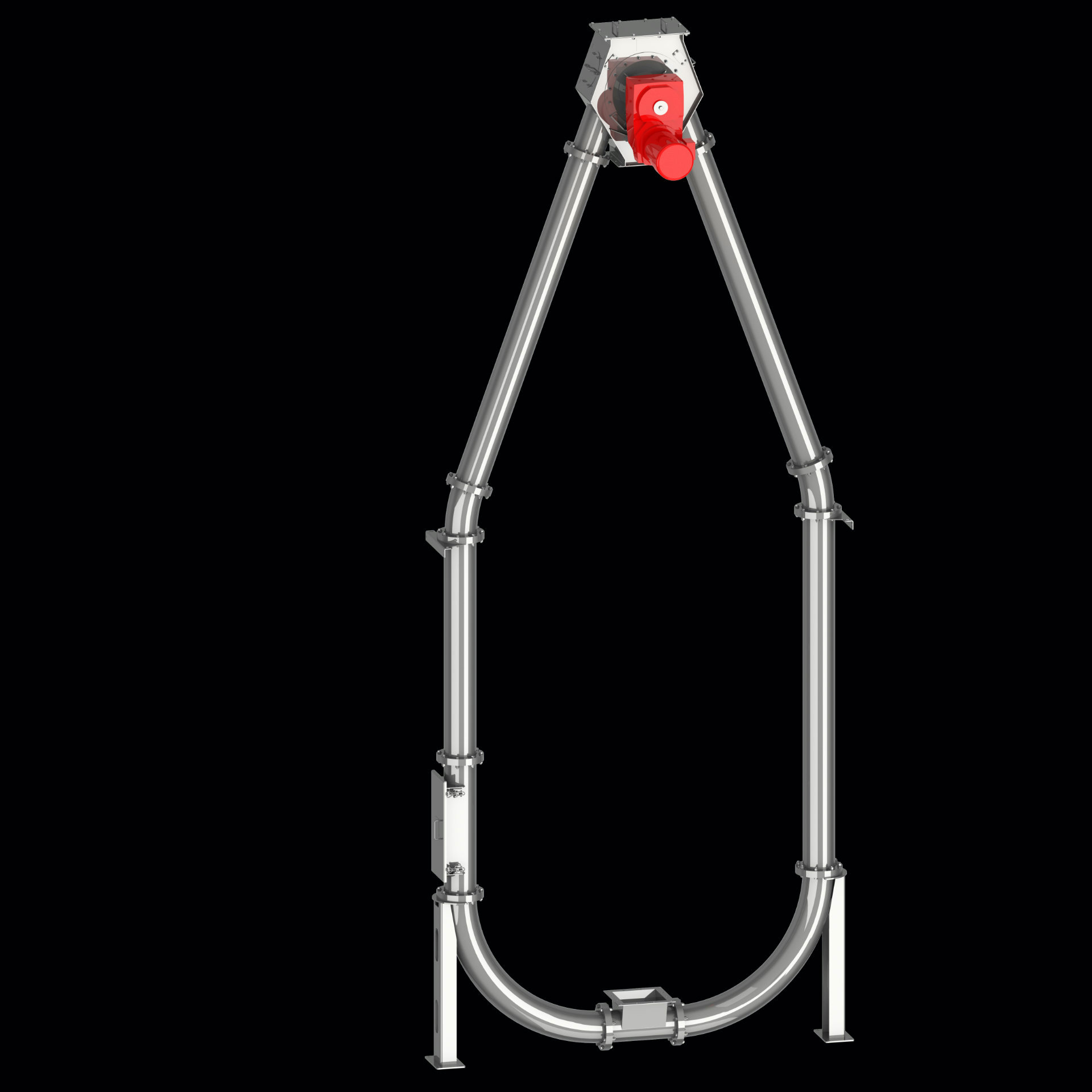
While many other conveyor systems experience problems with vertical conveyance routes, tube chain conveyors can be used for this purpose without any problems whatsoever. The small distance between conveyor discs (130 to 200 mm) forms “chambers” in the vertical tube that catch any material slipping from the chambers above them. This enables tube chain conveyors to achieve up to 100 % of their theoretically calculated delivery rates.
For vertical conveyance arrangements, only the conveyor chain, the drive station, the tube, and the tube bends are required.
A tensioning station is not needed, since the chain will tension itself through its own weight (this reduces the system's cost).
Their line layout, which can be configured in the shape of a pear, has also proven time and time again to be of great use in emptying big bags, returning conveyor belt residues back to the belt, etc. Also, vertical chain conveyors are frequently used for filling silos.
Horizontaal transport
They also have multiple advantages when they are used in horizontal conveyance arrangements and also in arrangements with customized changes of direction. Depending on the existing know-how regarding the materials to be conveyed and the mechanical loading capacity of the individual components involved, multiple changes of direction can be implemented in a single conveyor route by using tube bends or a redirecting station. When equipped with their basic components only, tube chain conveyors are extremely low-maintenance. So much so, in fact, that a number of companies have reportedly forgotten to perform maintenance on them altogether. Only the chain tension and the conveyor’s consumables need to be visually checked (through the corresponding service openings), and only at large intervals at that.
Transportsystemen
A transportation system consists of a transportation unit, a means of transportation, and the transportation process. The term “transportation system” refers to both internal (i.e., within a facility) and outside systems. Since the transitions between them are blurry, the concepts are often used synonymously. The transportation unit is also referred to as a conveyor unit or loading unit. Meanwhile, the means of transportation is referred to as a means of conveyance, especially in internal applications. Similarly, the system is also called a material flow system or conveyor system internally.